鲁晨光中文主页 English Homapage Papers on ArXiv Recent papers about Semantic Information and Statistical Learning
2020年9月发表的一篇重要的科学哲学文章
这篇文章英文版应Philosophies的专刊Logic anf Science的客座编辑Dr. Fabien Paillusson的邀请而写(不收版面费)。
他邀请我是因为看到我发表在Entropy上关于确证的文章:https://www.mdpi.com/1099-4300/22/4/384 .
应邀文章是一个大统一文章:
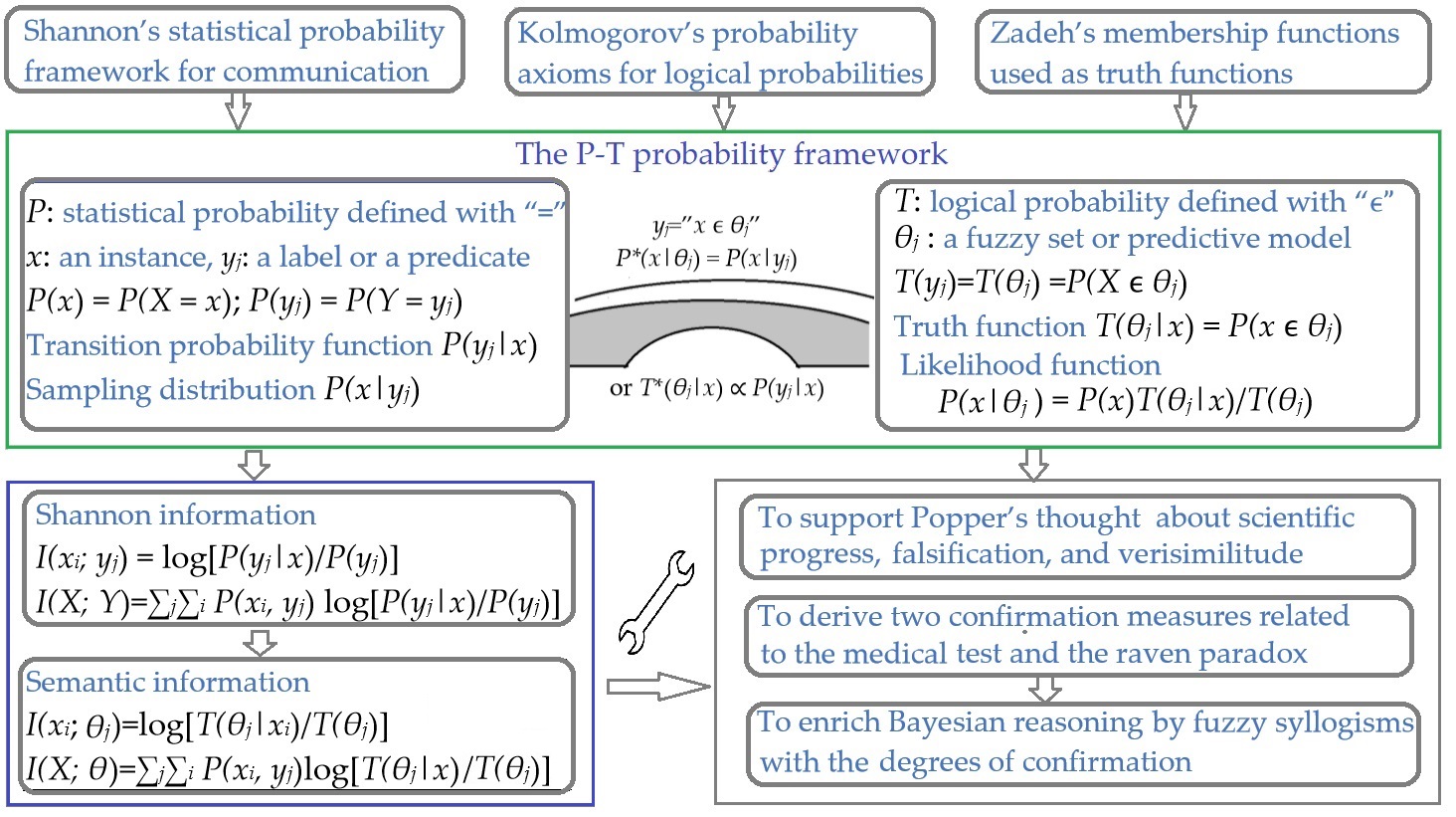
1. 统计和逻辑的统——了解人工智能中统计学派和逻辑学派的分歧的人更能理解这一统一的重要性;
2. 归纳(包括确证)和证伪的统一——这是从休谟开始由来已久的被认为是难以调和的科学哲学问题;
3. Shannon 信息论和Popper科学进化论的统一。
这篇文章将会产生怎样影响?......至少斯坦福哲学百科全书的许多词条要改写或补充(几个词条见:概率的解释,语义信息,确证, 逼真度, 逻辑和概率, 归纳逻辑)
点击词条可见西方相关研究背景和前沿。有比较才能鉴别!
| 中文:
P-T概率框架用于语义通信,证伪,确证和贝叶斯推理 (pdf) 手机版 摘要: 很多研究者想通过合理地定义逻辑概率或概率逻辑统一概率和逻辑;而本文试图统一统计和逻辑,以便我们可以同时使用统计概率和逻辑概率。为此,本文提出P-T概率框架——它是用Shannon的概率框架(用于电子通信)、Kolmogorove的概率公理(用于逻辑概率)和Zadeh的隶属函数(用作真值函数)组装的。推广的贝叶斯定理可以连接两种概率,用它我们可以将似然函数和真值函数相互转换;据此,我们可以用统计中的样本分布训练逻辑中的(模糊)真值函数。这一概率框架是在作者在语义信息、统计学习和颜色视觉的长期研究中发展而成的。本文首先介绍P-T概率框架并且通过其应用于语义通信解释其中不同概率,然后解释我们如何将这一概率框架和语义信息方法应用于统计学习、统计力学,假设评价(包括证伪)、确证和贝叶斯推理。这些理论上的应用显示了这一概率框架的合理性和实用性。这一概率框架将有助于可解释的人工智能。为解释神经网络,我们需要进一步研究。
|
English: The P–T Probability Framework for Semantic Communication, Falsification, Confirmation, and Bayesian Reasoning (Entropy website)
Abstract: Many researchers want to unify probability and logic by defining logical probability or probabilistic logic reasonably. This paper tries to unify statistics and logic so that we can use both statistical probability and logical probability at the same time. For this purpose, this paper proposes the P–T probability framework, which is assembled with Shannon’s statistical probability framework for communication, Kolmogorov’s probability axioms for logical probability, and Zadeh’s membership functions used as truth functions. Two kinds of probabilities are connected by an extended Bayes’ theorem, with which we can convert a likelihood function and a truth function from one to another. Hence, we can train truth functions (in logic) by sampling distributions (in statistics). This probability framework was developed in the author’s long-term studies on semantic information, statistical learning, and color vision. This paper first proposes the P–T probability framework and explains different probabilities in it by its applications to semantic information theory. Then, this framework and the semantic information methods are applied to statistical learning, statistical mechanics, hypothesis evaluation (including falsification), confirmation, and Bayesian reasoning. Theoretical applications illustrate the reasonability and practicability of this framework. This framework is helpful for interpretable AI. To interpret neural networks, we need further study.
Keywords:
statistical probability; logical probability; semantic information; rate-distortion; Boltzmann distribution; falsification; verisimilitude; confirmation measure; Raven Paradox; Bayesian reasoning
|
Graphical Abstract: